CCleaner is a legitimate system clean-up software solution which fell victim to hackers who inserted rouge code into the program’s free version, sometime between March 11th and July 4th 2017. It is believed a group of Chinese state-sponsored hackers breached Piriform’s network via a TeamViewer account, searched for CCleaner distribution servers, and then released a CCleaner update tainted with malware.
Patched
The official CCleaner (v5.33) binary was patched with malicious code using the TLS Callback method. Every binary has an entrypoint where code starts to execute, the TLS Callback method allows code to be executed before this entrypoint, allowing malicious code to execute before the program begins
TLS Callback Method
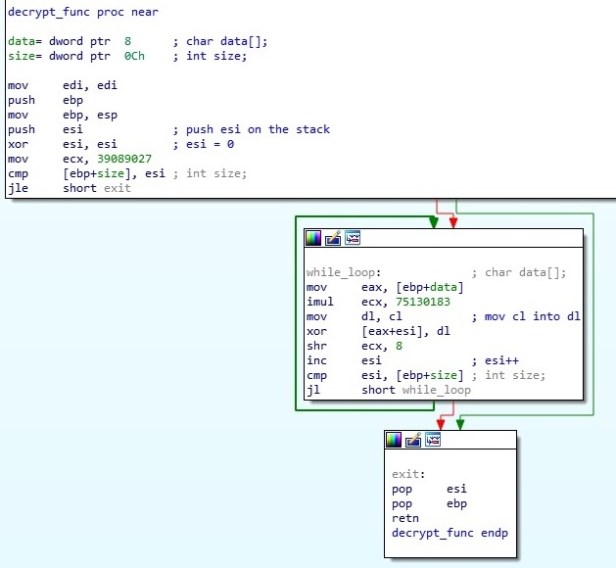
The TLS callback method can be used to execute malicious code prior to the entry point of the main program. The TLS Callback starts at (0x0040102C) this code is responsible for decrypting data which contains the two stages of the malicious payload, a PE loader as well as a DLL file that functions as the malware payload.
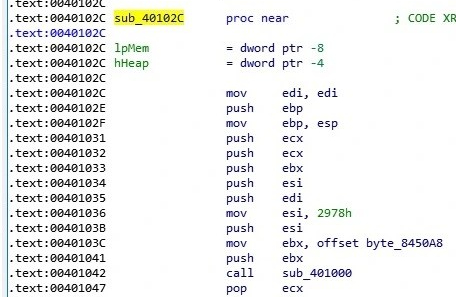
Sub_4040102C (0x0040102C)
Looking at this function in IDA PRO we see the following.
Looking at the assembly closely we see registers been pushed on the stack, a large hex number been placed in the esi register, that pushed on the stack, byte code been placed in ebx and that put on the stack followed by a function been called. This looks straight off to be a buffer with its size and payload been placed on the stack and that called by the function sub_401000. By renaming this function and adding comments this is more understandable.
Looking at the payload more closely we see it’s encrypted.
The payload is a DLL stored encrypted (XOR) without the PE header (to avoid AV detections), and once loaded it fires a new thread that will run the malware code.
PE Loader
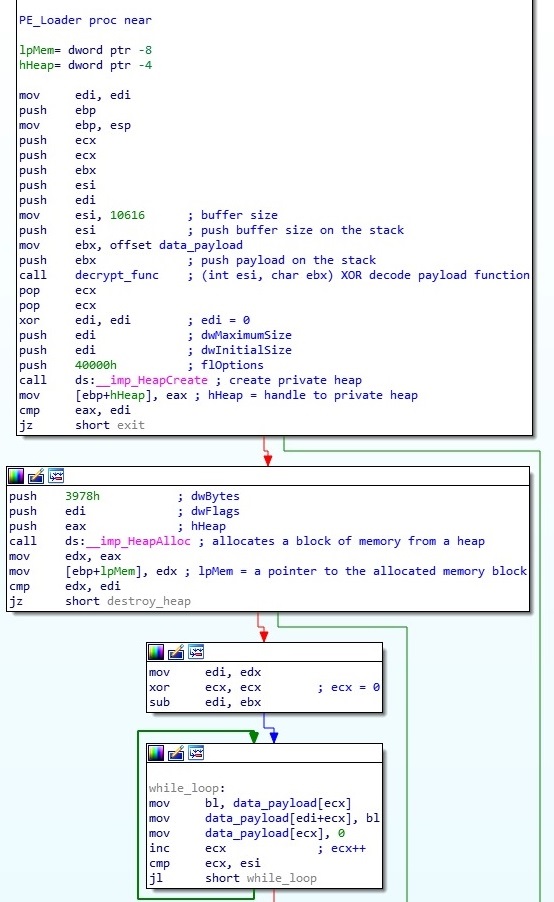
Analyzing the rest of the code, the malware is executing what appears to be a PE Loader, using Heap creation and execution. The binary then creates an executable heap using HeapCreate space is than allocated to this new heap which is where the contents of the decrypted data containing the malware is copied. As the data is copied to the heap, the source data is erased. The PE Loader is than called and begins its operation. Once the infection process has been initiated, the binary erases the memory regions that previously contained the PE loader and the DLL file, frees the previously allocated memory, destroys the heap and continues on with the normal CCleaner operations.
How that we know Sub_4040102C (0x0040102C) main purpose is to act as a PC Loader, we can rename it as such. Using the tool Relyze Desktop we can examine the execution flow of the PE loader making it better understood.

Looking at the code we can understand the logic better:
- Decrypt the payload using xor decryption.
- Space is than allocated to this new heap which is where the contents of the decrypted data containing the malware are copied.
- Once loaded it will execute the malware code.
- The malware is erased.
- The binary erases the memory regions that previously contained the PE loader and the DLL file.
- Frees the previously allocated memory, destroys the heap.
- Continues on with the normal CCleaner operations.
The DLL
CCleaner was comprised to deliver the Floxif malware as an injected DLL. Floxif malware builds a complete picture of the infected device and a complete picture of the local network. The malware gathers information of the running processes, installed software, mac addresses and network interfaces. This information is useful for targeting vulnerable system, running outdated versions of programs containing known vulnerabilities. All information is gathered and sent back to the hackers C2 servers. The hackers were looking for high profile targets, large tech organizations, such as Google or Microsoft, which they could steal source code, software applications, or any data they may deem useful.